A Comprehensive Approach to Tackling SCD in India
Introduction: Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) represents a significant global health challenge, with a notably severe impact in India, particularly among its tribal communities. As the country ranks second globally in terms of SCD prevalence, the need for improved access to modern medications is urgent.
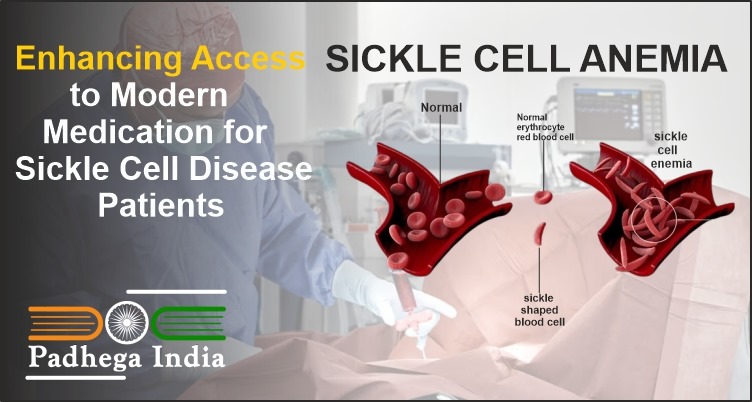
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease: SCD encompasses a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by an abnormality in the hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport in the blood. Due to a genetic mutation, red blood cells take on a rigid, sickle shape, which can obstruct blood flow and lead to severe pain, organ damage, and other serious health issues.
The Burden of SCD in India: With approximately 1 in every 86 births affected, IndiaтАЩs tribal populations face a disproportionate burden due to geographic isolation and socioeconomic disparities. This high prevalence underscores the need for targeted health interventions and policy support.
Treatment Advances: Recent years have seen significant advancements in SCD treatment. Beyond traditional pain management and blood transfusions, new medications and breakthroughs in gene therapy are now offering disease-modifying and potentially curative treatments. These developments represent a paradigm shift in the approach to managing the disease.
Challenges in Accessibility: Despite these advancements, accessing these new treatments remains a significant challenge for many. Hydroxyurea, a key medication proven to reduce complications in SCD patients, is not universally available. Addressing this gap requires a concerted effort from healthcare providers, government agencies, and pharmaceutical companies.
Importance of Collaboration: Global collaboration is crucial in advancing research and treatment options for SCD. Leveraging IndiaтАЩs large patient population and robust pharmaceutical sector can drive significant progress in this field. Initiatives that focus on widespread screening, improving drug accessibility, and supporting cutting-edge gene therapy research are essential.
Community Empowerment: It is vital to empower affected communities through culturally sensitive health initiatives. Engaging tribal communities directly can improve the effectiveness of early screening and interventions, enhancing the overall health outcomes for individuals with SCD.
Path Forward: Investment in ongoing research, clinical trials, and the integration of new technologies such as AI and telemedicine are crucial. These efforts, combined with strong policy advocacy, are key to supporting comprehensive strategies like the National Sickle Cell Anemia Elimination Mission, which aims to eradicate SCD in India by 2047.
Conclusion: The combination of new treatments and collaborative efforts offers a promising outlook for the management and potential cure of SCD. With continued focus and innovation, significant strides can be made towards achieving health equity and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this challenging disease.
┬а
- Global Scenario: An estimated 20 million people worldwide suffer from SCD, with the prevalence and impact varying significantly by region.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing advances in gene therapy and precision medicine hold the potential to transform treatment modalities for SCD.
- Policy Initiatives: Legislative efforts and prioritization of healthcare resources are crucial for developing sustainable solutions and supporting the health needs of SCD patients.